The following infographics form part of the United States Studies Centre report, Australian AgTech: Opportunities and challenges as seen from a US venture capital perspective.
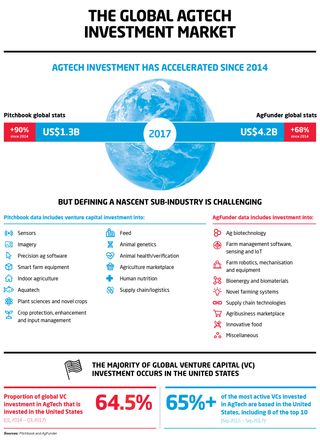
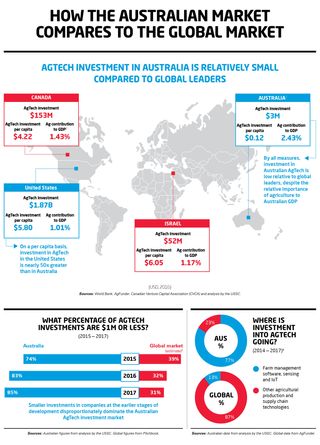
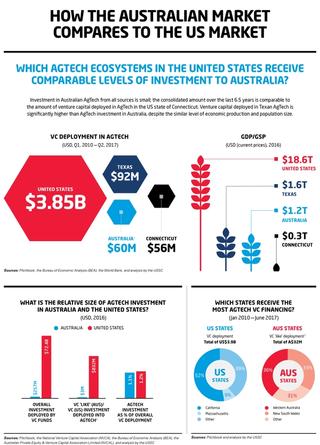
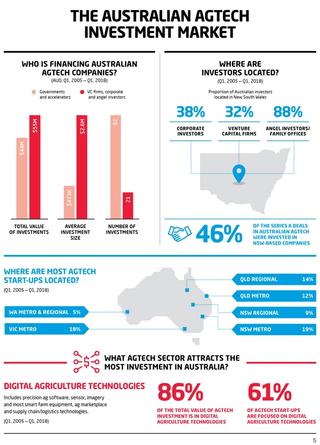
The following infographics form part of the United States Studies Centre report, Australian AgTech: Opportunities and challenges as seen from a US venture capital perspective.



